Studio-in-the-Cloud
Distributed rendering using render farms is a technique used in computer graphics to speed up the process of rendering images, animations, or simulations.
What is Distributed Rendering?
Distributed rendering involves splitting a rendering task into smaller parts and distributing these parts across multiple computers (nodes) to work on them simultaneously. This parallel processing significantly reduces the time required to complete the rendering.
What is a Render Farm?
A render farm is a collection of high-performance computers (often referred to as nodes) networked together to form a single powerful rendering unit. Each node in the farm contributes its processing power to the rendering tasks.
How It Works:
- Job Submission: The user submits a rendering job to the render farm through a rendering software or a farm management system.
- Job Distribution: The farm management software breaks down the rendering job into smaller tasks and distributes these tasks to available nodes in the farm.
- Rendering: Each node processes its assigned task. These tasks can be individual frames in an animation, sections of a single image, or elements of a simulation.
- Aggregation: Once all nodes complete their tasks, the results are collected and combined to form the final output.
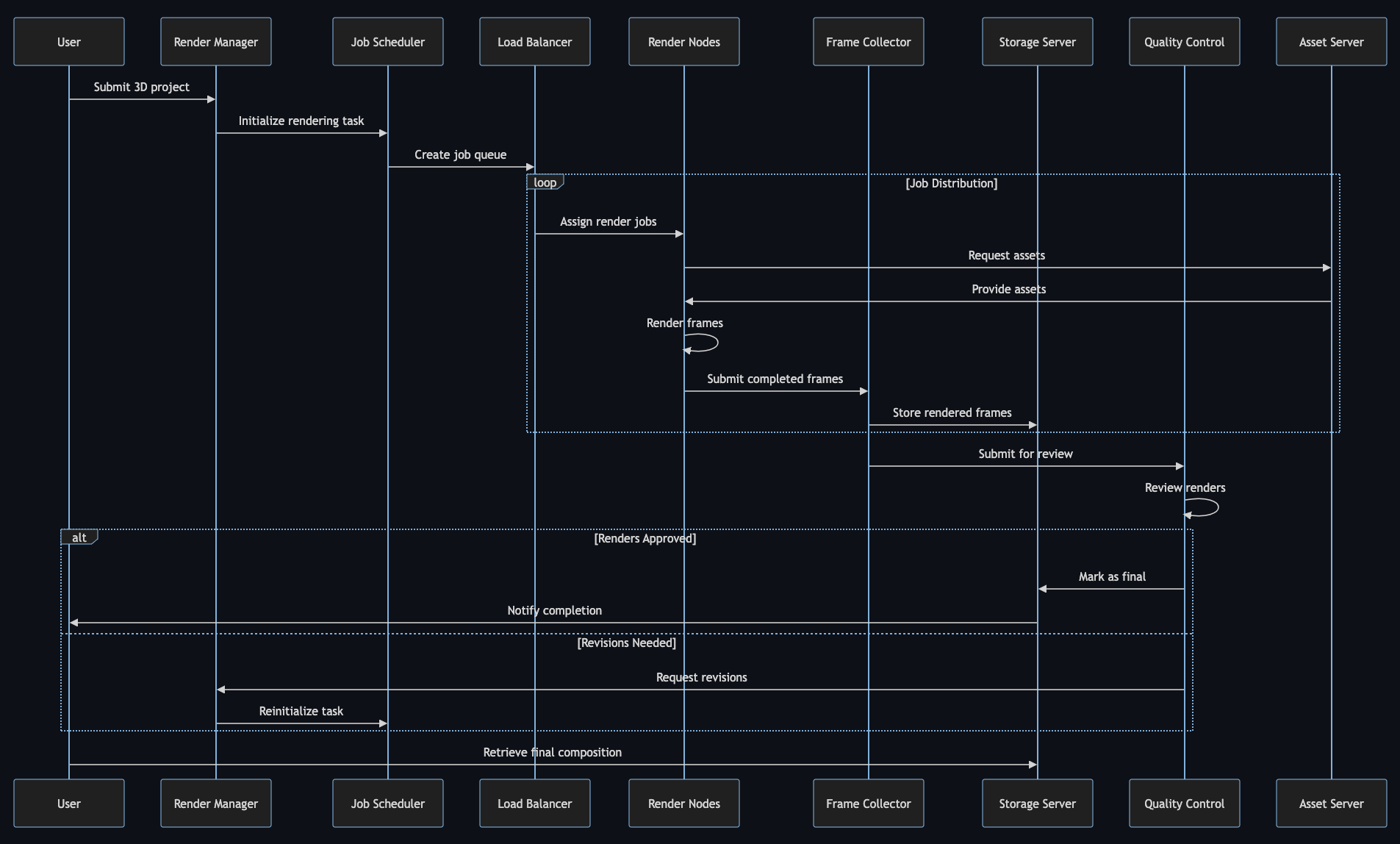
Render Farm Architecture
Benefits:
- Speed: Significantly reduces rendering time by leveraging the power of multiple machines.
- Efficiency: Optimizes the use of computational resources, especially for large and complex rendering tasks.
- Scalability: Easy to scale by adding more nodes to the farm as needed.
- Cost-Effective: Can be more economical than relying on a single high-end workstation for rendering.
Applications:
- Animation and VFX: Widely used in the film and gaming industries for rendering high-quality animations and visual effects.
- Architecture: Used for rendering detailed architectural visualizations and walkthroughs.
- Scientific Simulations: Employed in scientific research for rendering complex simulations and models.
Software and Tools:
- Render Farm Management Software: Tools like Thinkbox Deadline, Qube!, and Royal Render help manage and distribute rendering jobs across the farm.
- Rendering Engines: Commonly used rendering engines include Autodesk Arnold, Pixar’s RenderMan, and Chaos Group’s V-Ray.
Challenges:
- Setup and Maintenance: Requires a significant initial setup and ongoing maintenance to ensure all nodes function correctly.
- Resource Management: Efficiently managing and allocating resources to avoid bottlenecks and maximize productivity.
- Network Bandwidth: High demand on network bandwidth for transferring large amounts of data between nodes.